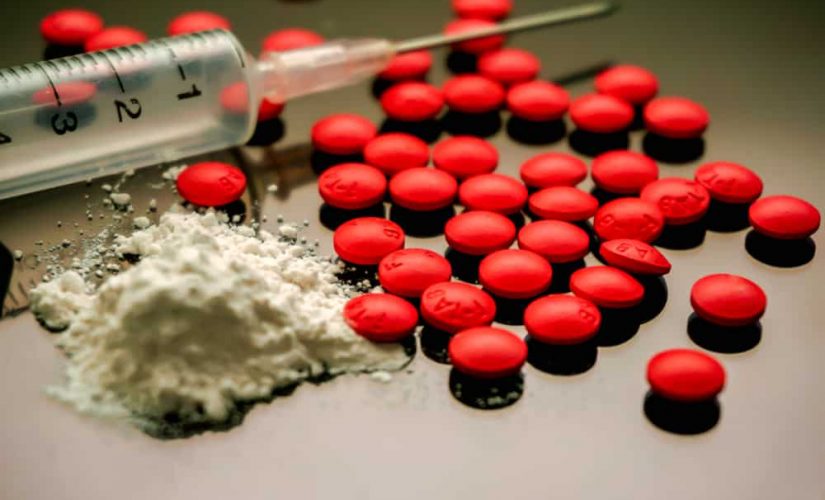

Ice is a stimulant drug, which means it speeds up the messages travelling between the brain and the body. It is a type of methamphetamine, which is generally stronger and more addictive and has more harmful side effects than the powder form known as speed.
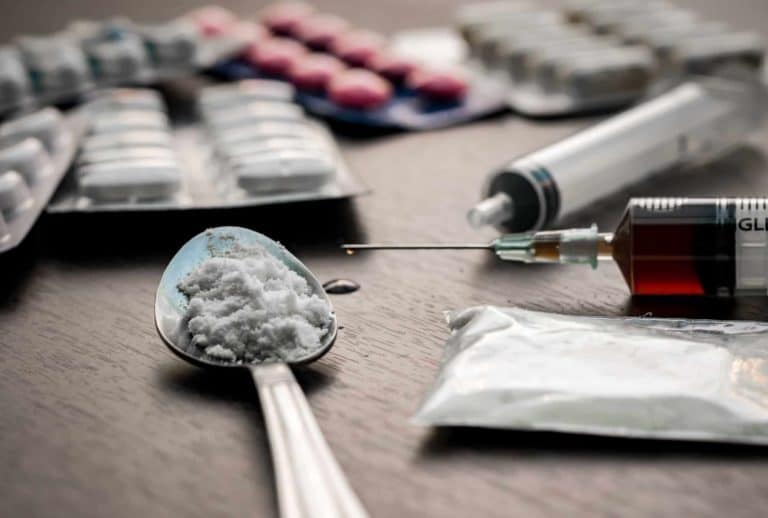
Ice usually comes as small chunky clear crystals that look like ice. It can also come as white or brownish crystal-like powder with a strong smell and bitter taste.1
Other names – Crystal meth, shabu, crystal, glass, shard
Ice is generally smoked or injected and the effects can be felt in 3 to 7 seconds. It is sometimes swallowed (15 to 30 minutes to feel the effects) or snorted (3 to 5 minutes to feel the effects).
There is no safe level of drug use. Use of any drug always carries some risk. It’s important to be careful when taking any type of drug. The effects of ice can last for around 6 hours, but it might be hard to sleep for a few days after using the drug.
Ice affects everyone differently, but effects may include:
Injecting ice and sharing needles can increase the risk of:
Snorting ice can damage the nasal passage and cause nose bleeds.
If you would like information on how we conduct drug testing please call us anytime on 1300 HAYDEN or 0403 428 523

The NSW economy is bustling and the construction industry is a major contributor to the

Hayden Workplace Testing is very proud to offer you a large range of services to
This article was posted by the Alcohol and Drug Foundation 24/08/16. Heroin deaths spike as
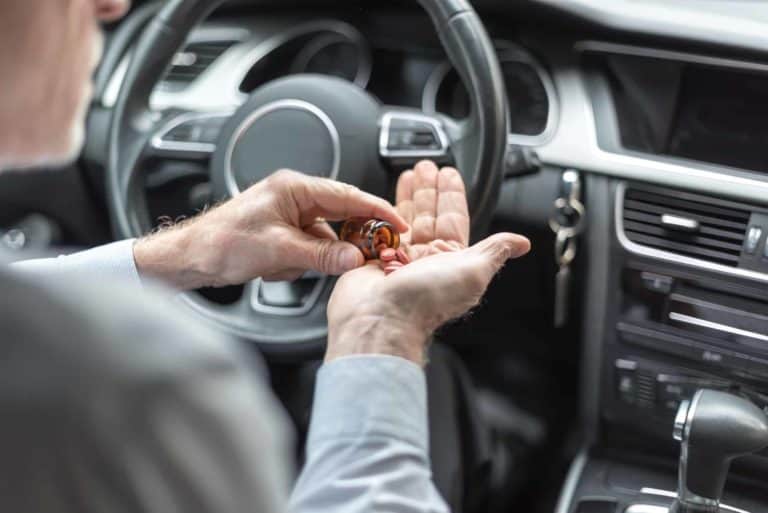

1/3 Hunter drivers test positive for drugs Police are concerned about the staggering amount of